Data Democracy in Supply Chain Management
Data democracy involves making data widely accessible and available to a broad range of individuals within organizations or society. It aims to eliminate barriers and empower people to access, analyze, and utilize data for informed decision-making. By promoting open access to data, data democracy enables individuals from diverse backgrounds and skill levels to understand and leverage its potential. It’s about giving everyone an equal opportunity to access and comprehend data, breaking down the exclusivity that often surrounds it. Ultimately, data democracy seeks to foster a more inclusive and participatory approach to data usage, where people can harness its insights and benefits to shape their decisions effectively.
Foundation Elements for Data Democracy
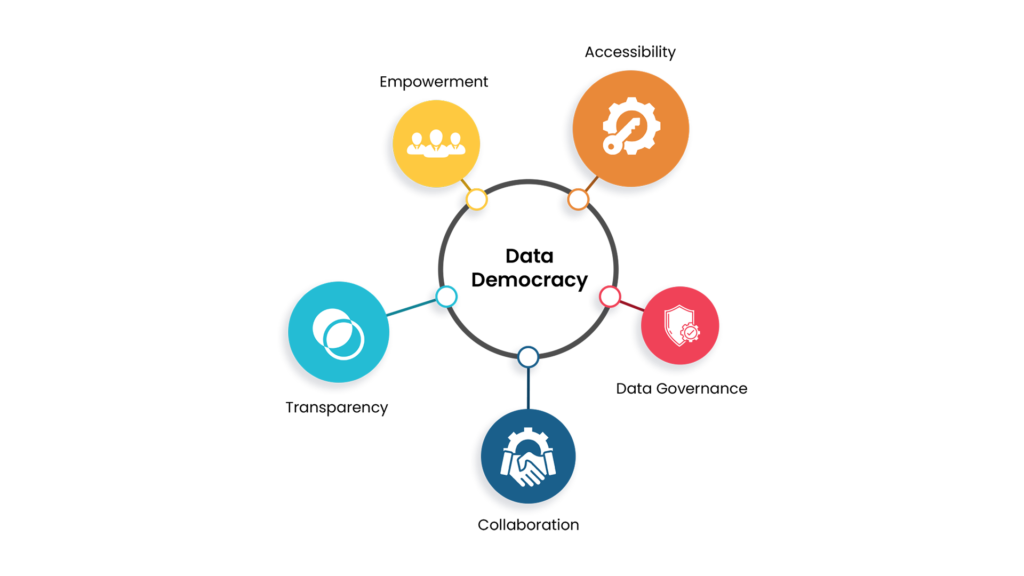
Benefits of Data Democracy in Supply Chain Operations
Data democracy brings a multitude of advantages. It allows organizations to make swift, well-informed decisions, fuels innovation and creativity, and boosts problem-solving capabilities. Moreover, it empowers individuals by equipping them with valuable insights to propel their work forward.
Note: Data democracy should be implemented thoughtfully and in line with relevant privacy regulations and data protection practices. Balancing accessibility with data privacy and security is essential to ensure the responsible use of data.
Data-driven Decision-making in Supply Chain through Data Democracy
Identify Key Data Stakeholders
Determine the primary individuals or groups within your organization or society who require access to data for making informed decisions. This includes personnel from different departments, teams, or hierarchical levels of the organization.
Evaluate Data Availability
Assess the current data sources and infrastructure within your organization. Identify the available data assets and evaluate their quality, reliability, and accessibility.
Establish Data Governance Policies
Formulate explicit policies and guidelines for data governance to ensure responsible and ethical use of data. Clearly define rules regarding data privacy, access controls, data sharing protocols, and security measures to safeguard sensitive information. This step is vital for fostering trust and compliance with regulations.
Develop Data Collection and Integration Processes
Create procedures and mechanisms for collecting relevant data from diverse sources. This may involve setting up data pipelines, implementing data integration techniques, and establishing connections with external data providers.
Optimize Data Storage and Management
Select appropriate technologies, such as data lakes or data warehouses, to efficiently store and organize data. Implement data management practices to ensure data quality, cleansing, and lineage.
Enhance Data Accessibility and Utilization
Design user-friendly interfaces and tools that enable stakeholders to access and interact with data. This could involve developing dashboards, visualizations, and self-service analytics platforms that cater to their specific analytical needs.
Promote Data Education and Training
Offer training programs and educational resources to enhance data literacy and analytical skills among stakeholders. Conduct workshops, provide online courses, or establish internal training initiatives to equip individuals with the knowledge and abilities required to comprehend and leverage data effectively.
Continuously Improve and Seek Feedback
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of data democracy initiatives. Seek feedback from stakeholders and make necessary improvements to enhance their experience and maximize the value derived from data.
Monitor and Measure Impact
Establish metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the impact of data democracy efforts. Monitor how data accessibility and insights contribute to informed decision-making, operational efficiencies, and overall organizational performance. Utilize this feedback to refine and optimize the data democracy process.
Enhancing Visibility and Transparency in the Supply Chain through Data Democracy
The key difficulty was to provide a Single Source of Truth. When dealing with large data from various sources, it’s often difficult to make sure the business is provided with accurate data from various systems. Designed a complete end-to-end framework where data is ingested from various sources into Data Warehouse. Various pipelines with different transformations are implemented making sure we have proper data lineage.
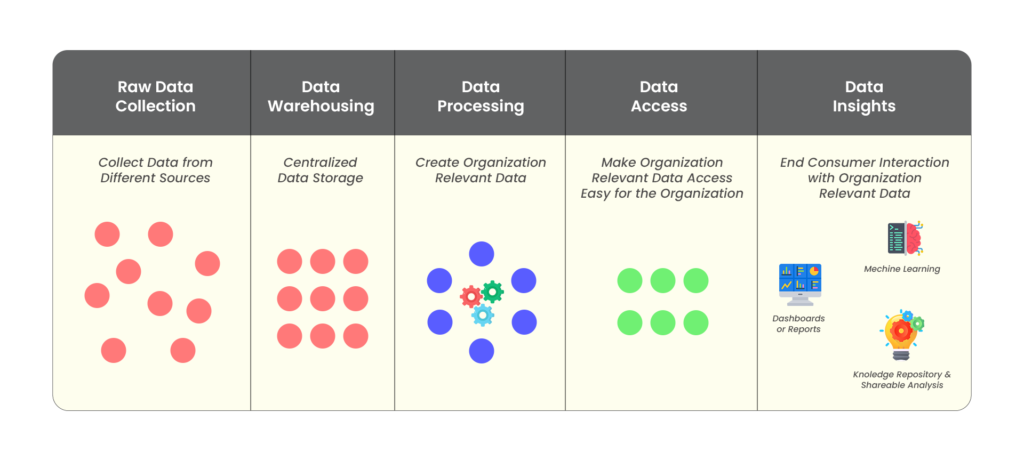
Democratizing Data for Better Supply Chain Performance
We used the following stack which includes Azure ADF, Azure Databricks, Azure Synapse. This is how we make sure we provide the right, accurate & consistent and near real-time data for users. Once data is available at L2 (Gold layer) we assisted businesses to use the right reporting tools like Tableau, and PowerBI to build reports and dashboards for visualizations. A constant support system is always the lifeline and to address business issues we have the proper ticketing model with minimal turnaround time.